- Getting Started
- Code Review
- Platforms
- Configuration
- CI integrations
- Design Tools
- Developer Tools
- Web Projects
- Get Notified
- API
API
- Getting Started
- Code Review
- Platforms
- Configuration
- CI integrations
- Design Tools
- Developer Tools
- Web Projects
- Get Notified
- API
Webhooks
Screenshotbot provides a mechanism to get notifications of events via webhooks. Webhooks are nothing but HTTP callbacks that are called from Screenshotbot to a service you own and operate.
Setting up webhooks
To set up webhooks, go to Settings -> Webhooks. Provide a Webhook endpoint, and check the Enable webhooks checkbox.
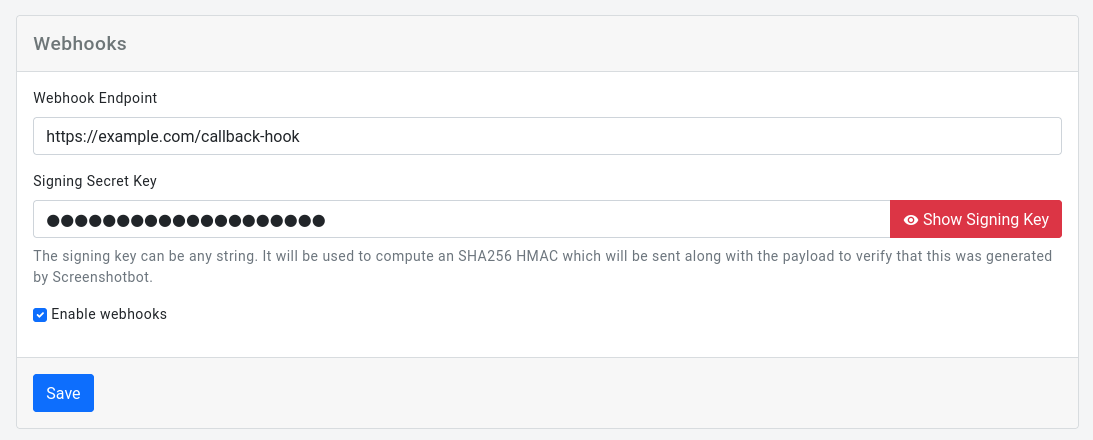
You can click the Show Signing Key to get the signing key Screenshotbot will use to sign every request. By verifying the signature of every payload, you can be sure that it was generated by us.
Secure your webhooks (recommended)
Screenshotbot sends a POST request to your service with the given payload. The payload is a JSON body, which we will describe in the next section.
Before you parse the JSON body, you might want to verify the payload. (You can skip this step if you're not doing anything sensitive with the event.)
Each request will have a header Screenshotbot-Signature that looks like t=%d,signature=%s. t is the unix timestamp in UTC when the payload was created. signature is HMAC-SHA256 of {t}.{payload}, using the signing key from the settings page.
To prevent replay attacks, you might want to verify that the timestamp in the signature was less than, say, five minutes in the past.
Debugging and Testing Webhooks
While building a service that listens to webhooks, you might have to test and debug the integration.
We provide a log of all the webhooks we have sent out in the last 30 days, and give you a way to inspect the payload that was sent, and also an option to resend failed payloads.
This let's you test your endpoint without having to manually reproduce the event in Screenshotbot each time.

Webhook events
Event channel.promotion
This event is dispatched when a promotion happens on a branch that resulted in a report.
This event has the following fields:
channel
The channel name on which this promotion happened.
branch
The git branch on which this promotion happened. e.g. `main`
run
The run that triggered this event
id
The ID of this run
channel
The channel name used with this run
screenshots
A list of screenshots for this run. This field may not be present when querying a run.
name
The name associated with this screenshot
imageId
The ID of the image associated with this screenshot
url
The URL to download the original image from
commit
The Git commit hash for this run
mainBranchCommit
The Git hash of the main branch at the time that this run was created.
buildUrl
The URL of the build job that created this run
mainBranch
The main branch, usually `main` or `master`.
gitlabMergeRequestIID
A GitLab merge request IID associated with the run, if any.
compareThreshold
The comparison threshold used for comparisons associated with this run.
comparePixelTolerance
The square of the euclidian distance between two pixels when considering them different or not.
url
The URL of this run
author
The author of this run. This is used when implementing policies around reviews.
metadata
A list of metadata elements. This information will typically not affect runs, but only for debugging.
shard
An optional shard-spec. This information is not present when reading a run. When creating a run, the presence of a shard-spec might delay the actual creation until all of the shards are available.
key
A unique, but arbitrary, identifier that identifies all the shards. For instance this might be the CircleCI root build id.
number
The number of the shard, 0-indexed.
count
The total count of shards
previousRun
The previous promoted run
id
The ID of this run
channel
The channel name used with this run
screenshots
A list of screenshots for this run. This field may not be present when querying a run.
name
The name associated with this screenshot
imageId
The ID of the image associated with this screenshot
url
The URL to download the original image from
commit
The Git commit hash for this run
mainBranchCommit
The Git hash of the main branch at the time that this run was created.
buildUrl
The URL of the build job that created this run
mainBranch
The main branch, usually `main` or `master`.
gitlabMergeRequestIID
A GitLab merge request IID associated with the run, if any.
compareThreshold
The comparison threshold used for comparisons associated with this run.
comparePixelTolerance
The square of the euclidian distance between two pixels when considering them different or not.
url
The URL of this run
author
The author of this run. This is used when implementing policies around reviews.
metadata
A list of metadata elements. This information will typically not affect runs, but only for debugging.
shard
An optional shard-spec. This information is not present when reading a run. When creating a run, the presence of a shard-spec might delay the actual creation until all of the shards are available.
key
A unique, but arbitrary, identifier that identifies all the shards. For instance this might be the CircleCI root build id.
number
The number of the shard, 0-indexed.
count
The total count of shards
report
The report object that was generated
id
The ID of this report
run
The ID of the run that generated this
channel
The channel name
title
The report title, something like `N changes, M added`
reviewState
The review status of the report. One of 'accepted', 'rejected', 'none' or 'na'.
reviewerName
If the review state 'accepted' or 'rejected', this will be the name of the reviewer
Event gitlab.update-build-status
If webhooks are enabled for GitLab integration, this webhook is dispatched each time we update your GitLab build status. This webhook is also dispatched if you don't provide us a GitLab access token, so it can be used to set up an integration with GitLab in a manner that restricts Screenshotbot's access to your GitLab.
This event has the following fields:
repoId
The repository ID. e.g. myorg/myproject. Typically, you'll url-encode this when passing it to the GitLab API. e.g. /projects/myorg%2Fmyproject/statuses/abcd0000.
sha
The commit SHA being updated
state
The state of the build status, one of: success, failed or pending
targetUrl
The URL to be linked to, typically a link to Screenshotbot report or a run.
name
The name of the build status. Typically it might just say "Screenshotbot" but if used with batching it might be something different.
description
The description of the build status